
Security News
PyPI Introduces Digital Attestations to Strengthen Python Package Security
PyPI now supports digital attestations, enhancing security and trust by allowing package maintainers to verify the authenticity of Python packages.
bignumber.js
Advanced tools
A library for arbitrary-precision decimal and non-decimal arithmetic
The bignumber.js package is a JavaScript library for arbitrary-precision decimal and non-decimal arithmetic. It allows for high-precision calculations that are necessary when dealing with very large or very small numbers that cannot be accurately represented with JavaScript's native Number type.
Arithmetic Operations
Perform precise arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
"use strict"; const BigNumber = require('bignumber.js'); let x = new BigNumber(123.4567); let y = new BigNumber('123456.7e-3'); let z = x.plus(y); console.log(z.toString()); // '246.9134'Chaining Methods
Allows for method chaining to perform multiple operations sequentially on a BigNumber instance.
"use strict"; const BigNumber = require('bignumber.js'); let result = new BigNumber('111.1111111').plus('0.0000001').times('3').sqrt().toPrecision(10); console.log(result); // '1.732050808'Comparison
Compare two BigNumber instances to determine the relational state.
"use strict"; const BigNumber = require('bignumber.js'); let a = new BigNumber('2'); let b = new BigNumber('3'); console.log(a.isLessThan(b)); // trueRounding
Round a BigNumber to a specified number of decimal places.
"use strict"; const BigNumber = require('bignumber.js'); let number = new BigNumber('123.4567'); let rounded = number.toFixed(2); console.log(rounded); // '123.46'Conversion
Convert a BigNumber to a different base or to a string representation.
"use strict"; const BigNumber = require('bignumber.js'); let number = new BigNumber('123456.789e-3'); let inBase10 = number.toString(10); console.log(inBase10); // '123.456789'Similar to bignumber.js, decimal.js is a library for arbitrary-precision Decimal arithmetic. It provides a similar API but focuses strictly on decimal numbers, whereas bignumber.js can handle non-decimal (base 2-36) numbers as well.
big.js is another arbitrary-precision arithmetic library. It is smaller and simpler than bignumber.js, but it does not include some of the more advanced features and functions that bignumber.js provides.
mathjs is an extensive math library for JavaScript and Node.js, which includes functionality for arbitrary-precision arithmetic. It offers a wider range of mathematical functions and data types compared to bignumber.js, but it is also larger in size.
A JavaScript library for arbitrary-precision decimal and non-decimal arithmetic.
toExponential, toFixed, toPrecision and toString methods of JavaScript's Number typetoFraction and a correctly-rounded squareRoot method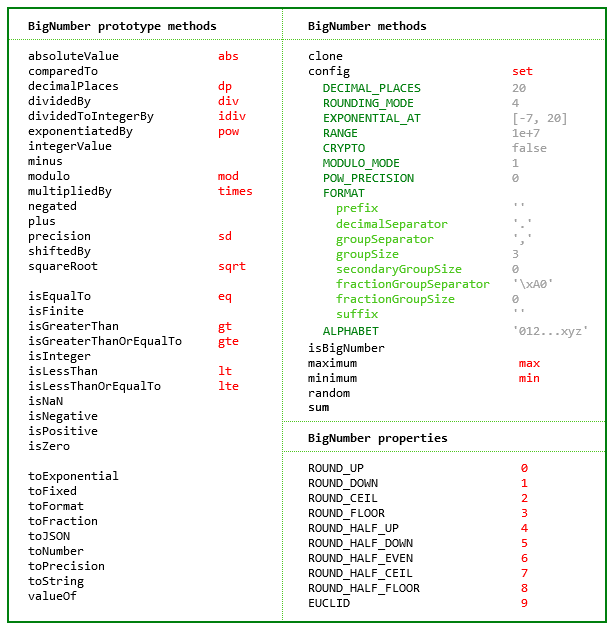
If a smaller and simpler library is required see big.js.
It's less than half the size but only works with decimal numbers and only has half the methods.
It also has fewer configuration options than this library, and does not allow NaN or Infinity.
See also decimal.js, which among other things adds support for non-integer powers, and performs all operations to a specified number of significant digits.
The library is the single JavaScript file bignumber.js or ES module bignumber.mjs.
<script src='path/to/bignumber.js'></script>
ES module
<script type="module">
import BigNumber from './path/to/bignumber.mjs';
Get a minified version from a CDN:
<script src='https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bignumber.js@9.1.2/bignumber.min.js'></script>
npm install bignumber.js
const BigNumber = require('bignumber.js');
ES module
import BigNumber from "bignumber.js";
import { BigNumber } from "./node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.mjs";
import BigNumber from 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mikemcl/bignumber.js/v9.1.2/bignumber.mjs';
import BigNumber from 'https://unpkg.com/bignumber.js@latest/bignumber.mjs';
The library exports a single constructor function, BigNumber, which accepts a value of type Number, String or BigNumber,
let x = new BigNumber(123.4567);
let y = BigNumber('123456.7e-3');
let z = new BigNumber(x);
x.isEqualTo(y) && y.isEqualTo(z) && x.isEqualTo(z); // true
To get the string value of a BigNumber use toString() or toFixed(). Using toFixed() prevents exponential notation being returned, no matter how large or small the value.
let x = new BigNumber('1111222233334444555566');
x.toString(); // "1.111222233334444555566e+21"
x.toFixed(); // "1111222233334444555566"
If the limited precision of Number values is not well understood, it is recommended to create BigNumbers from String values rather than Number values to avoid a potential loss of precision.
In all further examples below, let, semicolons and toString calls are not shown. If a commented-out value is in quotes it means toString has been called on the preceding expression.
// Precision loss from using numeric literals with more than 15 significant digits.
new BigNumber(1.0000000000000001) // '1'
new BigNumber(88259496234518.57) // '88259496234518.56'
new BigNumber(99999999999999999999) // '100000000000000000000'
// Precision loss from using numeric literals outside the range of Number values.
new BigNumber(2e+308) // 'Infinity'
new BigNumber(1e-324) // '0'
// Precision loss from the unexpected result of arithmetic with Number values.
new BigNumber(0.7 + 0.1) // '0.7999999999999999'
When creating a BigNumber from a Number, note that a BigNumber is created from a Number's decimal toString() value not from its underlying binary value. If the latter is required, then pass the Number's toString(2) value and specify base 2.
new BigNumber(Number.MAX_VALUE.toString(2), 2)
BigNumbers can be created from values in bases from 2 to 36. See ALPHABET to extend this range.
a = new BigNumber(1011, 2) // "11"
b = new BigNumber('zz.9', 36) // "1295.25"
c = a.plus(b) // "1306.25"
Performance is better if base 10 is NOT specified for decimal values. Only specify base 10 when you want to limit the number of decimal places of the input value to the current DECIMAL_PLACES setting.
A BigNumber is immutable in the sense that it is not changed by its methods.
0.3 - 0.1 // 0.19999999999999998
x = new BigNumber(0.3)
x.minus(0.1) // "0.2"
x // "0.3"
The methods that return a BigNumber can be chained.
x.dividedBy(y).plus(z).times(9)
x.times('1.23456780123456789e+9').plus(9876.5432321).dividedBy('4444562598.111772').integerValue()
Some of the longer method names have a shorter alias.
x.squareRoot().dividedBy(y).exponentiatedBy(3).isEqualTo(x.sqrt().div(y).pow(3)) // true
x.modulo(y).multipliedBy(z).eq(x.mod(y).times(z)) // true
As with JavaScript's Number type, there are toExponential, toFixed and toPrecision methods.
x = new BigNumber(255.5)
x.toExponential(5) // "2.55500e+2"
x.toFixed(5) // "255.50000"
x.toPrecision(5) // "255.50"
x.toNumber() // 255.5
A base can be specified for toString.
Performance is better if base 10 is NOT specified, i.e. use toString() not toString(10). Only specify base 10 when you want to limit the number of decimal places of the string to the current DECIMAL_PLACES setting.
x.toString(16) // "ff.8"
There is a toFormat method which may be useful for internationalisation.
y = new BigNumber('1234567.898765')
y.toFormat(2) // "1,234,567.90"
The maximum number of decimal places of the result of an operation involving division (i.e. a division, square root, base conversion or negative power operation) is set using the set or config method of the BigNumber constructor.
The other arithmetic operations always give the exact result.
BigNumber.set({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 10, ROUNDING_MODE: 4 })
x = new BigNumber(2)
y = new BigNumber(3)
z = x.dividedBy(y) // "0.6666666667"
z.squareRoot() // "0.8164965809"
z.exponentiatedBy(-3) // "3.3749999995"
z.toString(2) // "0.1010101011"
z.multipliedBy(z) // "0.44444444448888888889"
z.multipliedBy(z).decimalPlaces(10) // "0.4444444445"
There is a toFraction method with an optional maximum denominator argument
y = new BigNumber(355)
pi = y.dividedBy(113) // "3.1415929204"
pi.toFraction() // [ "7853982301", "2500000000" ]
pi.toFraction(1000) // [ "355", "113" ]
and isNaN and isFinite methods, as NaN and Infinity are valid BigNumber values.
x = new BigNumber(NaN) // "NaN"
y = new BigNumber(Infinity) // "Infinity"
x.isNaN() && !y.isNaN() && !x.isFinite() && !y.isFinite() // true
The value of a BigNumber is stored in a decimal floating point format in terms of a coefficient, exponent and sign.
x = new BigNumber(-123.456);
x.c // [ 123, 45600000000000 ] coefficient (i.e. significand)
x.e // 2 exponent
x.s // -1 sign
For advanced usage, multiple BigNumber constructors can be created, each with its own independent configuration.
// Set DECIMAL_PLACES for the original BigNumber constructor
BigNumber.set({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 10 })
// Create another BigNumber constructor, optionally passing in a configuration object
BN = BigNumber.clone({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 5 })
x = new BigNumber(1)
y = new BN(1)
x.div(3) // '0.3333333333'
y.div(3) // '0.33333'
To avoid having to call toString or valueOf on a BigNumber to get its value in the Node.js REPL or when using console.log use
BigNumber.prototype[require('util').inspect.custom] = BigNumber.prototype.valueOf;
For further information see the API reference in the doc directory.
The test/modules directory contains the test scripts for each method.
The tests can be run with Node.js or a browser. For Node.js use
npm test
or
node test/test
To test a single method, use, for example
node test/methods/toFraction
For the browser, open test/test.html.
To minify using, for example, terser
npm install -g terser
terser big.js -c -m -o big.min.js
The MIT Licence.
See LICENCE.
9.1.2
round to avoid bug in v8 Maglev compiler.minimum(0, -0) should be -0.FAQs
A library for arbitrary-precision decimal and non-decimal arithmetic
The npm package bignumber.js receives a total of 5,862,388 weekly downloads. As such, bignumber.js popularity was classified as popular.
We found that bignumber.js demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
PyPI now supports digital attestations, enhancing security and trust by allowing package maintainers to verify the authenticity of Python packages.

Security News
GitHub removed 27 malicious pull requests attempting to inject harmful code across multiple open source repositories, in another round of low-effort attacks.

Security News
RubyGems.org has added a new "maintainer" role that allows for publishing new versions of gems. This new permission type is aimed at improving security for gem owners and the service overall.